Architectural Refactorings
This section provides a documentation of all architectural refactorings (ARs) available in the Context Mapper tool.
Motivation: Why Refactoring?
The provided refactorings ensure that the result is always a correct CML model which compiles without errors. If you perform similar changes manually, you also have to fix errors that occur manually within the Context Map. The ARs ensure that corresponding references and dependencies in other parts of the model are respected and adjusted if necessary.
Architectural Refactoring Categories
The ARs are divided into the following categories:
- Structural Refactorings: Change the structure of the decomposition (impact on Bounded Contexts and/or Aggregates).
- Relationship Refactorings: Just change the type of a relationship on the Context Map, but do not change the structure of the decomposition.
Refactoring Overview
The Context Mapper tool offers you a set of architectural refactorings which can be applied to your CML models. The refactorings shall support you while evolving and improving the architecture of your system.
Structural Refactorings
We currently provide the following structural ARs:
| Name | Subject | Description | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR-1: Split Aggregate by Entities | Aggregate | Splits an aggregate which contains multiple entities and produces one aggregate per entity. | 1 Aggregate | n Aggregates |
| AR-2: Split Bounded Context by Features1 | Bounded Context | Splits a bounded context by grouping those aggregates together into one bounded context which are used by the same use case(s) and/or user stories (features). | 1 Bounded Context | n Bounded Contexts |
| AR-3: Split Bounded Context by Owner1 | Bounded Context | Splits a bounded context by grouping those aggregates together into one bounded context which belong to the same team. | 1 Bounded Context | n Bounded Contexts |
| AR-4: Extract Aggregates by Volatility | Bounded Context | Extracts all aggregates from a bounded context by a given volatility, or likelihood for change (RARELY, NORMAL or OFTEN), and moves them to a separate context. | 1 Bounded Context | 2 Bounded Contexts |
| AR-5: Extract Aggregates by Cohesion | Bounded Context | Extracts a set of aggregates which are chosen by certain cohesion criteria and moves them to a separate bounded context. | 1 Bounded Context | 2 Bounded Contexts |
| AR-6: Merge Aggregates | Aggregate | Merges two aggregates within a bounded context together to one aggregate. | 2 Aggregates | 1 Aggregate |
| AR-7: Merge Bounded Contexts | Bounded Context | Merges two bounded contexts together. The result is one bounded context containing all the aggregates of the two input boundedcontexts. | 2 Bounded Contexts | 1 Bounded Context |
| AR-8: Extract Shared Kernel | Shared Kernel relationship | Extracts a new bounded context for the common model parts of the Shared Kernel and establishes two upstream-downstream relationship between the new and the existing Bounded Contexts. | 1 Shared Kernel relationship | 1 New Bounded Context and 2 new upstream-downstream relationships |
| AR-9: Suspend Partnership | Partnership relationship | Suspends a Partnership relationship and replaces it with another structure how the two Bounded Context can depend on each other. The AR provides three strategies to suspend the partnership. | 1 Partnership relationship | Depends on the selected mode |
1: An aggregate in CML can be used by multiple features (use cases and/or user stories) and is owned by one owner (team).
Relationship Refactorings
The following ARs to change Context Map relationships are currently implemented:
| Name | Subject | Description | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR-10: Change Shared Kernel to Partnership | Shared Kernel relationship | Changes the type of a Shared Kernel relationship to a Partnership relationship. | Shared Kernel relationship | Partnership relationship |
| AR-11: Change Partnership to Shared Kernel | Partnership relationship | Changes the type of a Partnership relationship to a Shared Kernel relationship. | Partnership relationship | Shared Kernel relationship |
Examples
You can find input and corresponding output examples for all ARs listed above in our examples repository.
How to apply Architectural Refactorings
Visual Studio Code
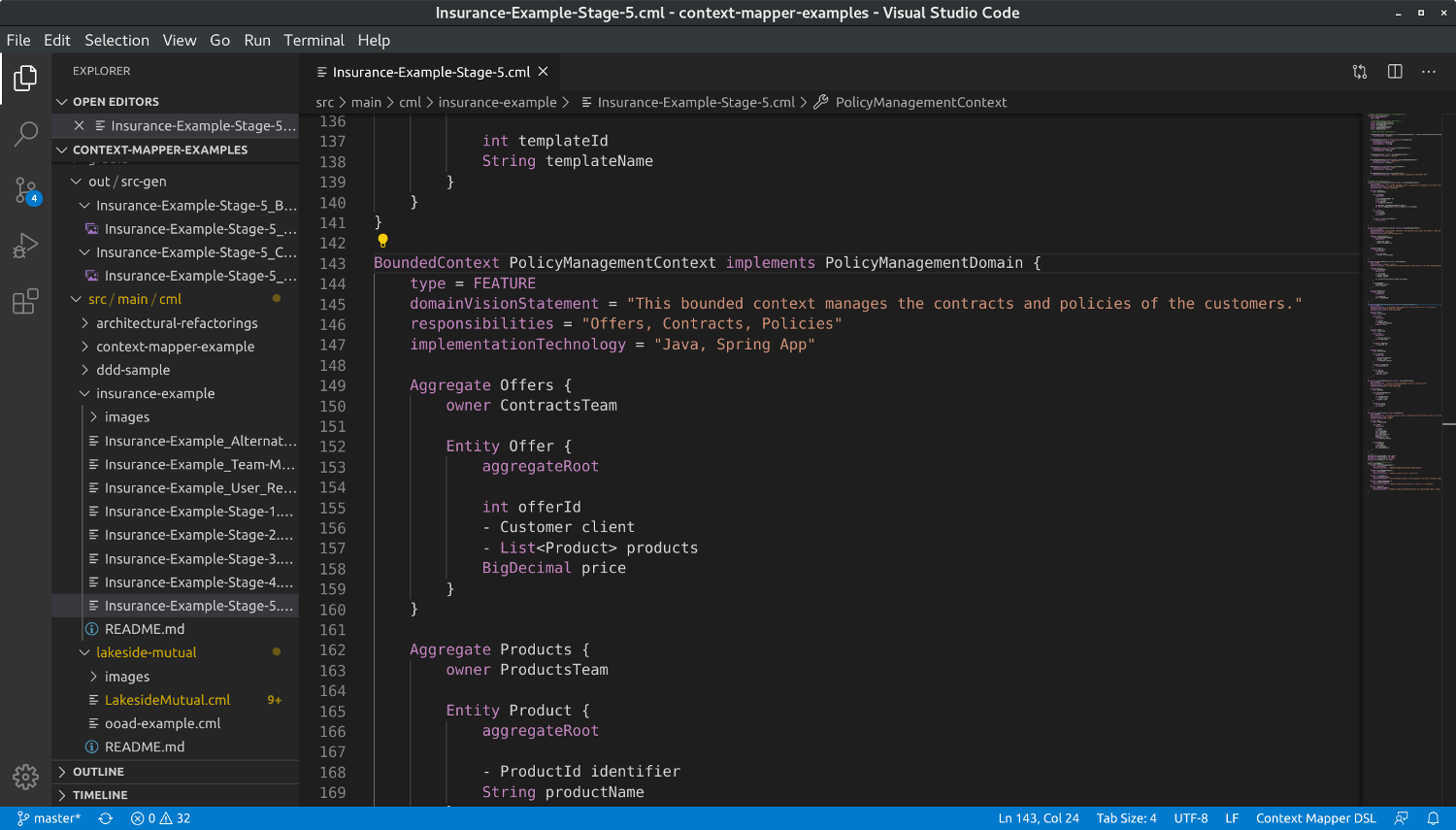
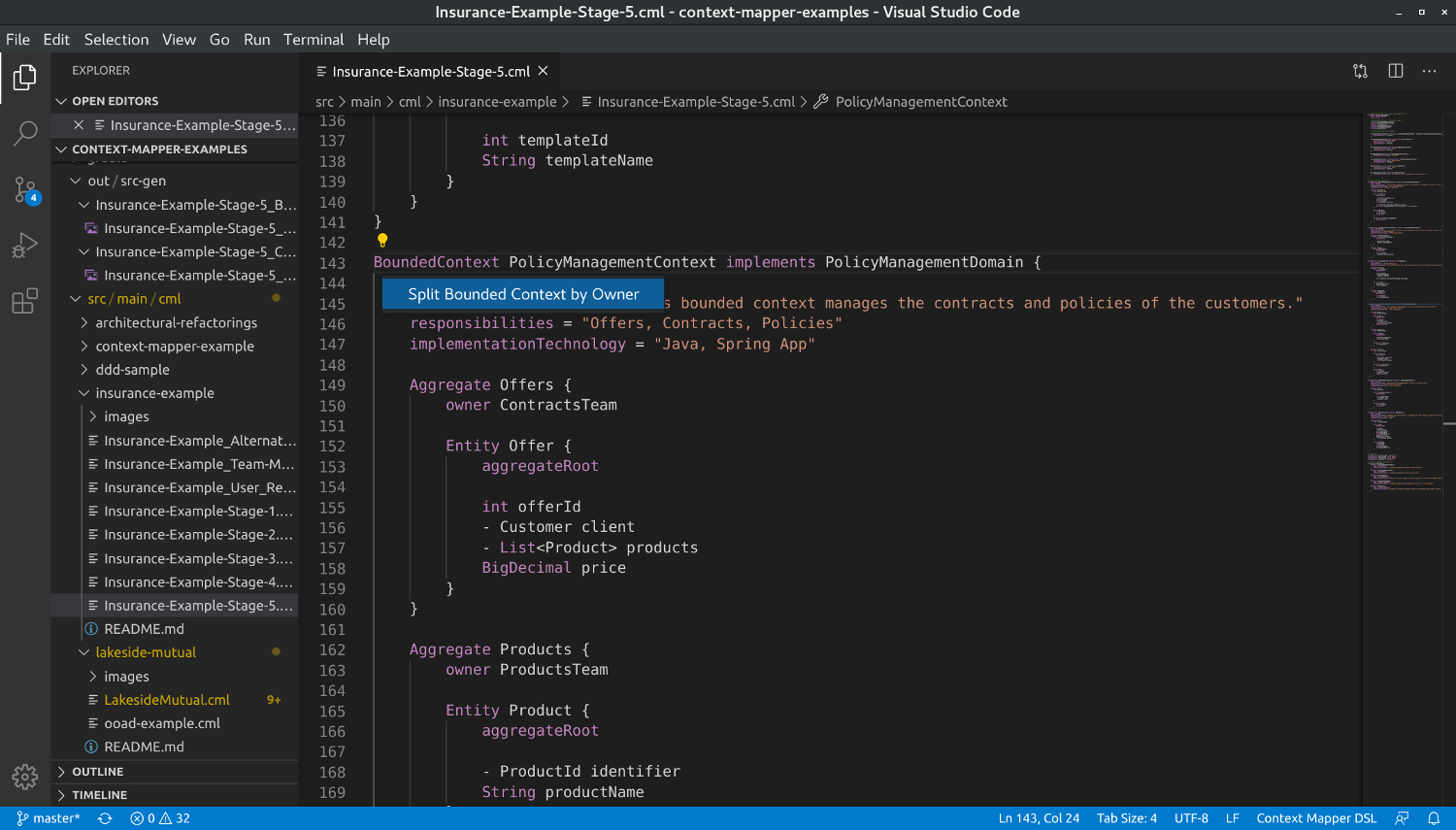
In VS Code we suggest the application of Architectural Refactorings via code actions. If your cursor is on a CML object on which an AR can be applied, a light bulb shows up:
In the case illustrated above, the PolicyManagementContext contains Aggregates that are maintained by different teams and Split Bounded Context by Owner (AR-3) can be applied:
By clicking on the light bulb and the AR you want to apply the model will be refactored accordingly.
Eclipse
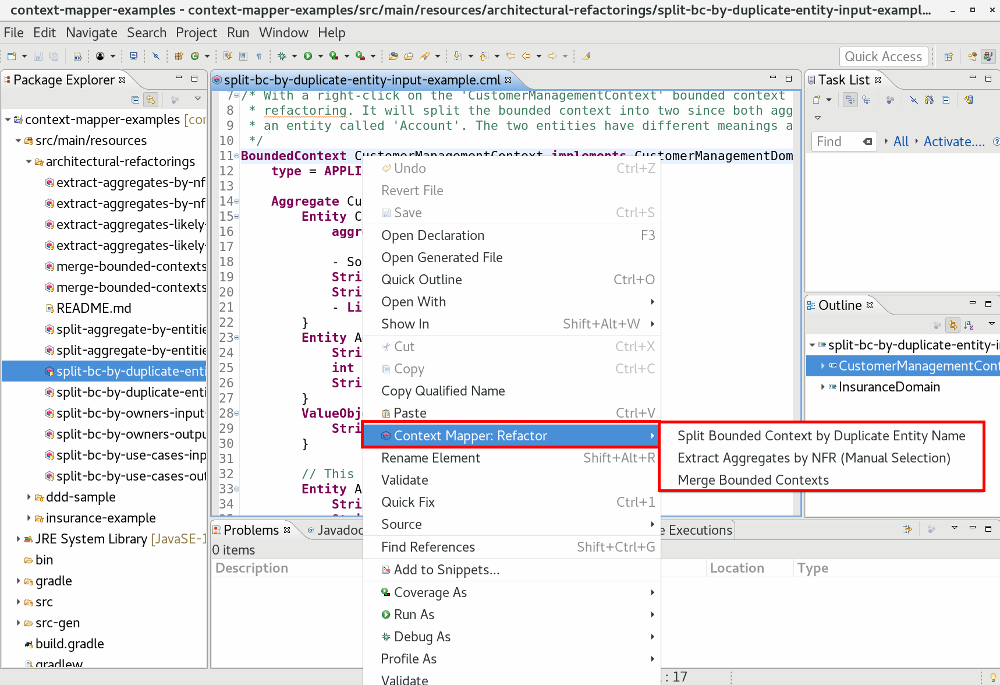
Architectural refactorings can be applied within the Context Mapper Eclipse plugin by using the context menu in the DSL editor. With a right-click on a bounded context or an aggregate the Context Mapper: Refactor menu entry appears and lists all refactorings which are applicable to the selected elements:
You can also use the Shift-Alt-T keybinding for quick access to the available refactorings (the cursor must be on the object on which you want to start the refactoring).
Note: The context menu only shows ARs for which your selected model element fulfills the preconditions. The preconditions for all ARs are mentioned on the corresponding detail pages linked above.