AR-1: Split Aggregate by Entities
Splits an aggregate which contains multiple entities and produces one aggregate per entity.
Context & Rationales
On the level of entities we typically try to group attributes or nanoentities in the terminology of ServiceCutter together, which belong to the same identity and share a common lifecycle. Thereby we aim to reduce the coupling between the entities and increase the cohesion within the entities.
- See also: Coupling criterion Identity and Lifecycle Commonality of ServiceCutter.
The same approach can be applied on the aggregate level. The aggregates within one bounded context shall be structured in a way which reduces coupling between the aggregates and increases the cohesion within them.
As your bounded context develops you may face the problem that an aggregate contains entities which exhibit an unsatisfying cohesiveness. In such a case you may want to split your aggregate into multiple aggregates in order to improve coupling and cohesion.
Goal
This Architectural Refactoring (AR) splits an aggregate and creates one aggregate for each entity. This AR can be applied when the entities within an aggregate exhibit unsatisfying cohesiveness and you decide to create multiple aggregates for the single entities.
Inverse AR’s:
Preconditions
- The input aggregate must contain at least two entities.
Input
- The aggregate which shall be split.
Output
- Multiple aggregates which contain one entity each.
- All entities become aggregate roots within their own aggregates.
Example
The following example illustrates how this AR can be applied. The corresponding sources can be found in our examples repository.
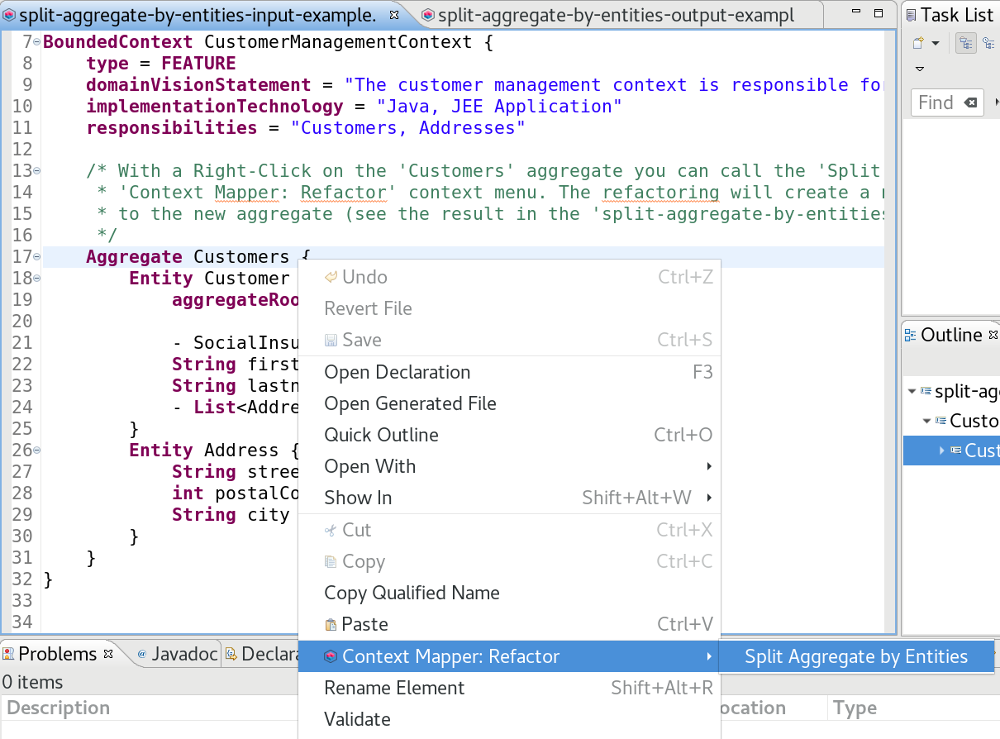
Input
In this example we have an aggregate containing two entities. The AR is available on the aggregate:
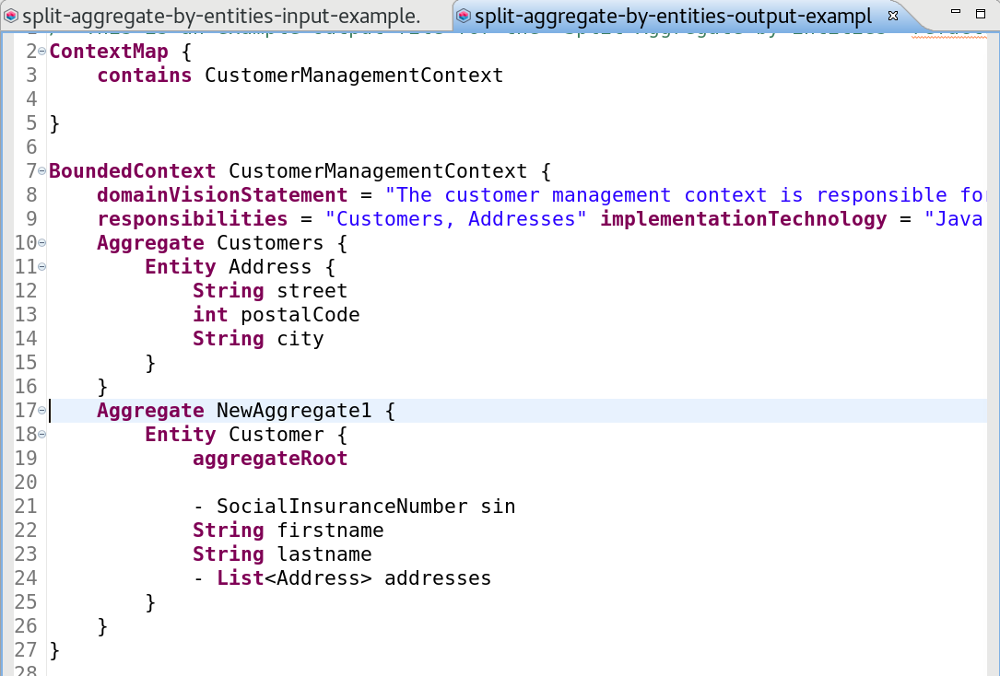
Result
The resulting bounded context contains two aggregates, one for each entity:
Example Sources
- You can find the CML sources for this AR example here.