AR-2: Split Bounded Context by Features
Splits a bounded context by grouping those aggregates together into one bounded context which are used by the same features: use case(s) and/or user stories.
Hint: An aggregate in CML can belong to multiple use cases and/or user stories (therefore the plural Features in the AR name).
Context & Rationales
By decomposing a system into multiple bounded contexts we aim for loose coupling between the bounded context and a high cohesion within them. One approach to achieve this and to decompose a system into components or (micro-) services is to split by use cases and/or user stories.
See also:
- Coupling criterion Semantic Proximity of ServiceCutter
- How to decompose the application into services? by Chris Richardson
- Single responsibility principle
In Context Mapper you can assign multiple use cases and/or user stories to an aggregate, which allows you to model by which features an aggregate is used. Consult our aggregate documentation page to see how this can be modeled in CML. The user requirements page documents how you specify your user stories and/or use cases.
Goal
This Architectural Refactoring (AR) splits a bounded context by features (or user requirements). This means, it creates bounded contexts containing aggregates which are used by the same use cases and/or user stories. It can be applied if your model exhibits a bounded contexts with aggregates which are used by different cases/stories.
Inverse AR’s:
Preconditions
- The bounded context must contain at least two aggregates.
- The aggregates must be assigned to different use cases and/or user stories.
Input
- One bounded context.
Output
- The AR creates multiple bounded contexts. Each bounded context contains one or more aggregates which are used by the same use cases and/or user stories.
Example
The following example illustrates how this AR can be applied. The corresponding sources can be found in our examples repository.
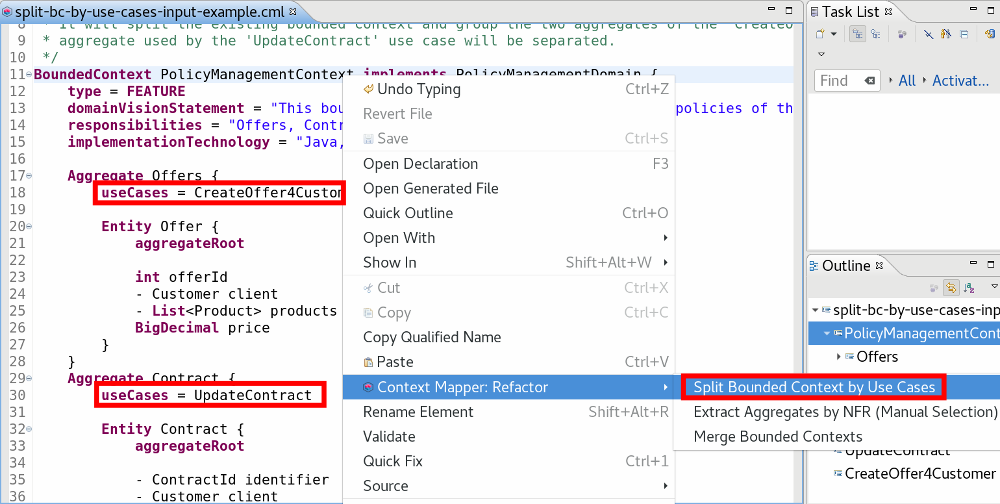
Input
The example bounded context contains two aggregates which are used by different use cases. The AR is available on the bounded context:
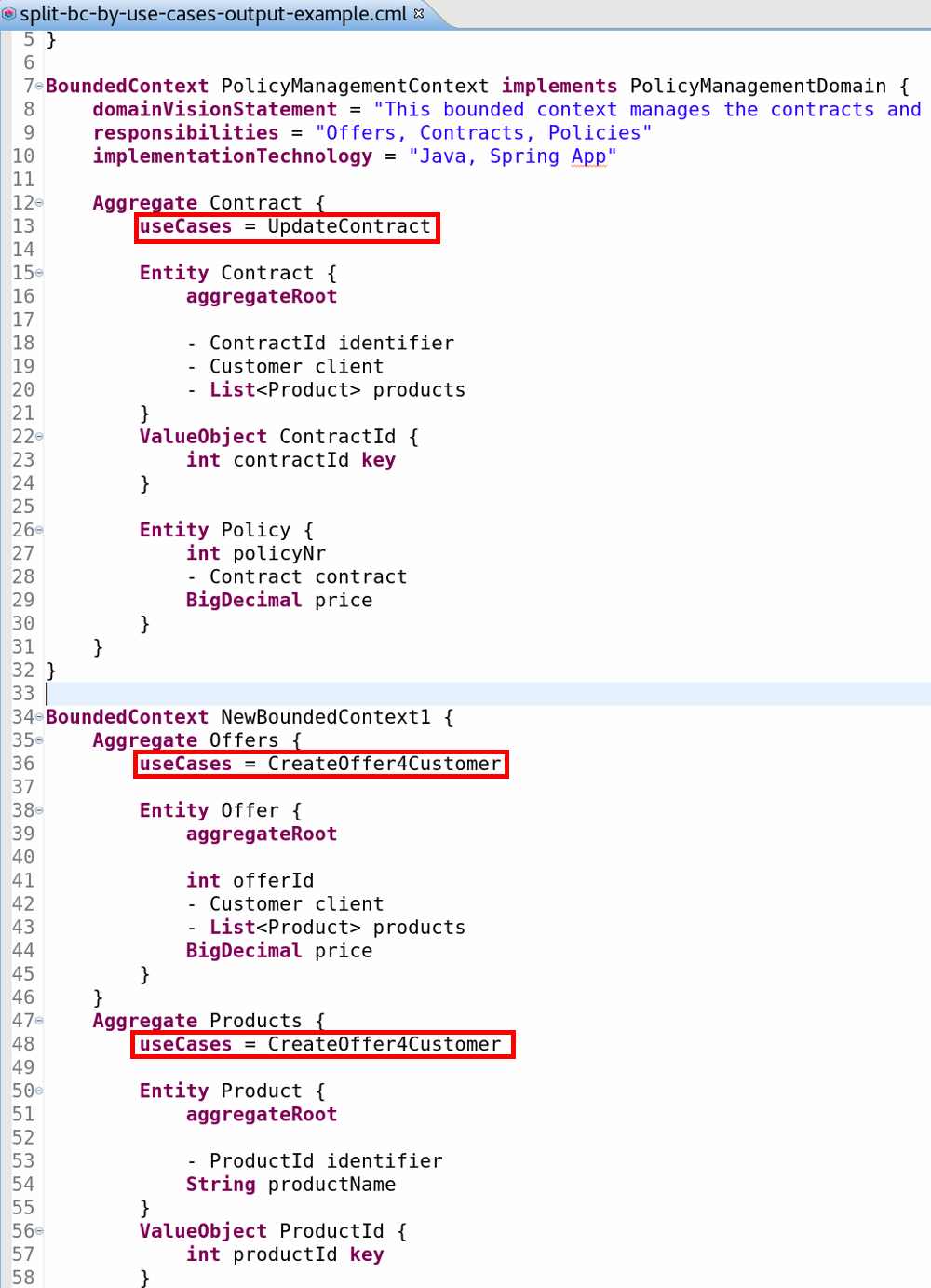
Result
The resulting model contains two bounded contexts, one for each use case:
Example Sources
- You can find the CML sources for this AR example here.