Stakeholders
The CML language supports the modelling of stakeholders of (digital) solutions and/or projects. This feature has been introduced to support the Value-Driven Analysis and Design (VDAD) process. One part of this process supporting ethical software engineering is the identification of all relevant stakeholders. For more information about the whole process we refer to the VDAD page. However, modelling stakeholders can support your requirements engineering process in different ways; no matter whether you apply VDAD practices or not.
Note: With our PlantUML generator you can automatically generate Stakeholder Maps, once you modelled all your stakeholders and stakeholder groups. See example below.
Stakeholders Container
On the root level of a CML file, one first needs to create a Stakeholders container. This can be done as simply as follows:
Stakeholders {
// add stakeholders and stakeholder groups here
}
However, if you want to model the stakeholders for a specific Bounded Context, you can declare that as follows:
BoundedContext ExampleContext Stakeholders of ExampleContext { // add stakeholders and stakeholder groups here }
Stakeholders
Inside a Stakeholders container, you can define your stakeholders. This can be done with the Stakeholder keyword an the name of the stakeholder:
BoundedContext ExampleContext
Stakeholders of ExampleContext {
Stakeholder Shopper
Stakeholder Software_Engineer
Stakeholder Architect
// etc.
}
In addition, you can provide additional information for a stakeholder using the description, influence and interest keywords:
BoundedContext ExampleContext
Stakeholders of ExampleContext {
Stakeholder Shopper {
description "Is using the shopping system to by everday goods."
influence MEDIUM
interest HIGH
}
}
The description just describes why and/or how the stakeholder uses the system or is impacted by the system. As suggested by many stakeholder mapping tutorials (see Miro or Mural), you can define what the influence of the stakeholders is and how much they are interested (interest) in the new system or feature.
Stakeholder Groups
Stakeholder maps often group stakeholders of similar roles or with similar interest together. This is also possible in CML with the StakeholderGroup keyword, which can again contain stakeholders with the Stakeholder keyword:
BoundedContext ExampleContext
Stakeholders of ExampleContext {
StakeholderGroup Online_Shopping_Company {
Stakeholder Development_Team {
influence MEDIUM
interest HIGH
}
Stakeholder Product_Management {
influence HIGH
interest HIGH
}
Stakeholder Customer_Relationship_Manager {
influence HIGH
interest MEDIUM
}
}
Stakeholder Shopper {
description "Is using the shopping system to by everday goods."
influence MEDIUM
interest HIGH
}
}
Visualization: Stakeholder Map
Once your stakeholders are modelled in CML, you can generate a visual stakeholder map automatically. Here is an example:
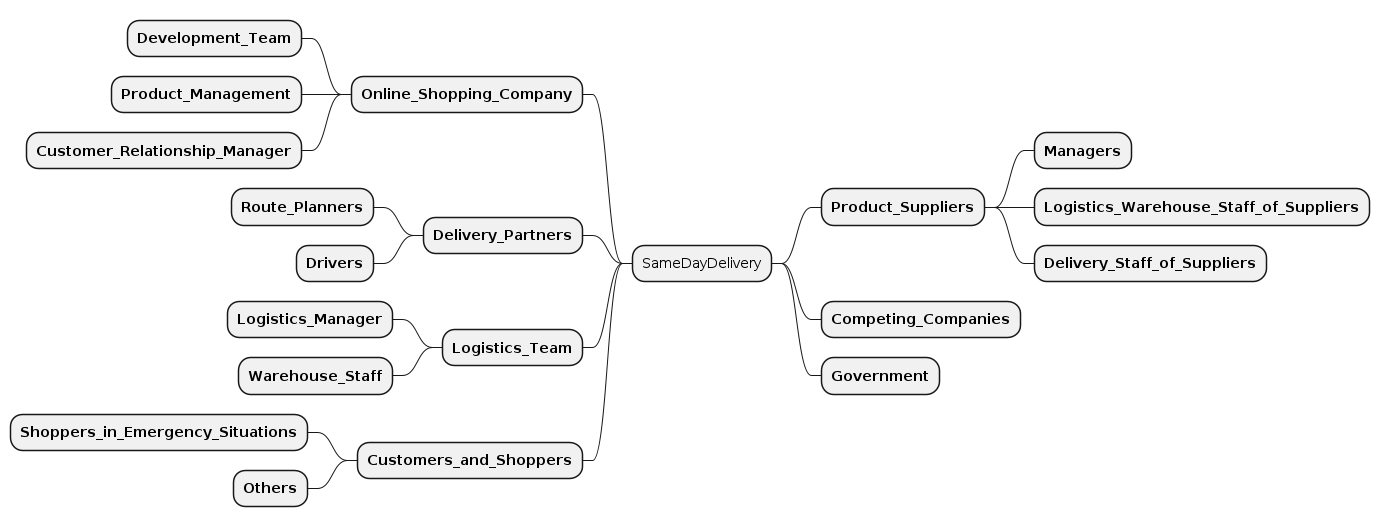
Check out our PlantUML generator on how to generate such a diagram.
Stakeholders Export to CSV
In addition to the Stakeholder Map visualization, you can export your modelled stakeholder data as a CSV file. To do so, use the Freemarker temple here together with our Generic Generator (Freemarker Templating).
Transformations
Note that we offer several transformations that might help modelling stakeholders and their values according to VDAD (Value-Driven Analysis and Design) more efficiently. The transformations are documented on the following page: Stakeholder and Value Modelling Transformations